
diamond coating process
Raman spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy of the nanocrystalline diamond-coated ring after mechanical fatigue testing indicated that the coating was in good condition. Kremer and co-workers (2008) investigated the machinability of two Al/SiC particulate MMC with 5 and 15% vol. Several methods for preparing diamond-based MEMS, including conformal coating, selective deposition, and lithographic patterning, have been described.40,41 Diamond film can be deposited as a thin, conformal coating using chemical vapor deposition. Sumant, in Diamond-Based Materials for Biomedical Applications, 2011. Scanning electron micrograph of freestanding ultrananocrystalline diamond propellers, which were grown by selective deposition followed by potassium hydroxide etching on silicon posts. The multilayer nanocrystalline/microcrystalline/nanocrystalline diamond film showed better wear resistance than the single layer nanocrystalline diamond film. However, translation of these devices towards medical use has been limited. dlc coating coatings carbon diamond hardness structure This often results in premature failure of the cutting edge by coating delamination and spalling. The process allows a film deposition of synthesised diamond with a high growth speed, at low energy consumption. Andrewes et al. demonstrated adhesion, growth, and viability of GT1-7 neuronal cells (neuronal line of hypothalamic origin) on diamond surfaces.46 Cells plated on H or O terminated nanocrystalline diamond samples were shown to adhere, proliferate, and exhibit somatic Ca2+ activity. Huang et al. Fig. conductivity composites microstructure sintering coatings diamond amorphous carbon engineerlive suited applications industrial better coating Diamond is also an attractive material for use in cell-based biosensors. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the worn pins revealed multiple protuberances of polyethylene rising above the surface in polyethylene-on-CoCr, and a single, large, elevated protuberance in polyethylene-on-NSD. From: Diamond-Based Materials for Biomedical Applications, 2013, S.A. Catledge, Y.K. The tensioned cutting blade has a hole, which is coated with diamond particles. Fig. Iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), and nickel (Ni) are the well-known examples of this category of substrate. Free-standing diamond windows have been prepared using CVD technique [73,81].  To characterize such an interface a cross-sectional TEM study would be informative. The FIB technique can be used to prepare such a cross-section. Researchers showed that nanocrystalline diamond can exhibit improved properties in micromechanical machines (MEMS and NEMS devices), surface acoustic wave devices, biological cell cultures and for DNA detection. These temperatures will possibly render the O-rings ineffective. When wafers are measured after stress relief, they have quite a large taper and warp/bow, and values are larger if the wafer is thin. deposited nanocrystalline diamond coatings on Si3N4bioglass substrates using hot filament chemical vapor deposition.35 Pin-on-flat wear studies in Hanks balanced salt solution and dilute fetal bovine serum provided coefficient of friction values of 0.010.02 and 0.060.09, respectively; the higher wear rate obtained with fetal bovine serum was attributed to attachment of proteins. ID-cutting offers good flexibility in small-lot production, since it makes a wafer at a time, being suitable also for processing short ingot pieces. 5.7, no statistically significant difference in wear factor was found between polyethylene against NSD-(H), NSD-(He) and CoCr. Arrays of solution-gate field-effect transistors were fabricated by Dankerl et al. Diamond-coated metallic wires and/nonmetallic fibers because of their stiffness may find application in aerospace engineering. 70. SEM pictures of a self-supporting diamond helix and tube. plating electroless depositing Rezek et al.
To characterize such an interface a cross-sectional TEM study would be informative. The FIB technique can be used to prepare such a cross-section. Researchers showed that nanocrystalline diamond can exhibit improved properties in micromechanical machines (MEMS and NEMS devices), surface acoustic wave devices, biological cell cultures and for DNA detection. These temperatures will possibly render the O-rings ineffective. When wafers are measured after stress relief, they have quite a large taper and warp/bow, and values are larger if the wafer is thin. deposited nanocrystalline diamond coatings on Si3N4bioglass substrates using hot filament chemical vapor deposition.35 Pin-on-flat wear studies in Hanks balanced salt solution and dilute fetal bovine serum provided coefficient of friction values of 0.010.02 and 0.060.09, respectively; the higher wear rate obtained with fetal bovine serum was attributed to attachment of proteins. ID-cutting offers good flexibility in small-lot production, since it makes a wafer at a time, being suitable also for processing short ingot pieces. 5.7, no statistically significant difference in wear factor was found between polyethylene against NSD-(H), NSD-(He) and CoCr. Arrays of solution-gate field-effect transistors were fabricated by Dankerl et al. Diamond-coated metallic wires and/nonmetallic fibers because of their stiffness may find application in aerospace engineering. 70. SEM pictures of a self-supporting diamond helix and tube. plating electroless depositing Rezek et al.  Fabrication of wafer-size crystals may potentially enhance the properties of diamond for its further biomedical applications.
Fabrication of wafer-size crystals may potentially enhance the properties of diamond for its further biomedical applications. 
 Copyright 2022 Elsevier B.V. or its licensors or contributors. This material may be used to prevent release of metal ions, inhibit fibrous tissue growth, and prevent blood coagulation in medical devices. Biosensing is vastly expanding in the medical field, especially, with increased pressure for biomedical solutions for detection and biomarking.
Copyright 2022 Elsevier B.V. or its licensors or contributors. This material may be used to prevent release of metal ions, inhibit fibrous tissue growth, and prevent blood coagulation in medical devices. Biosensing is vastly expanding in the medical field, especially, with increased pressure for biomedical solutions for detection and biomarking.  The diamond electrode array, which interfaced directly with the retinal ganglion cells, was the key implanted material enable when placed to epiretinally interface with both the neural cells but also with head mounted camera offering the best performance and safety for patients. Nebel et al. Amaral et al.
The diamond electrode array, which interfaced directly with the retinal ganglion cells, was the key implanted material enable when placed to epiretinally interface with both the neural cells but also with head mounted camera offering the best performance and safety for patients. Nebel et al. Amaral et al. 
 As a result, diamond films on ceramics and metals tend to have residual stress in the films that often leads to spallation of the coating. However, there is a serious issue of poor diamond nucleation on the surface of WC tools containing small amount of cobalt due to ready dissolution of carbon into cobalt [73]. Adapted from A.K. hfcvd cvd diamond dental system coatings burs tools derived hard schematic producing modified could figure azom No degradation in DNA bonding was noted over 30 hybridization/denaturation cycles. Plate-like topography is favored for tribological applications because of lower abrasive effects. dlc coating equipment machine tool pecvd introduction carbide manufacturer Markku Tilli, in Handbook of Silicon Based MEMS Materials and Technologies (Second Edition), 2015. In addition, potassium currents of HEK293 cells were activated with the patch-clamp technique and observed with field-effect transistors. Diamond has been shown to limit the release of toxic ions and therefore increase the longevity of the implant. Although diamond offers many opportunities for biomedical use, the progress in diamond and diamond-coated implantables remains at a steady pace, with future avenues for diamond-breakthroughs being in bionics and in hermetic capsules where micro/nano devices are currently at high need. Pecheva et al. As a result, a large amount of carbon is being transported into the bulk, rather than remaining at the substrate surface and promotes diamond nucleation. Dua, D.D. However, good adhesion between the substrate and the coating is mandatory for effective tribological applications, which in turn demands an agreeable match between their coefficients of thermal expansion. Cobalt chromium alloys however are susceptible to ion release under prolonged wear. 8.12 shows the picture (adapted from Ref. The microspikes increased the mechanical lysis efficiency for B16-F10 (ATCC CRL-6475) murine melanoma cells compared with non-textured glass. 14. It is interesting to note that performance of the microspikes did not diminish after multiple ultrasonic vibration/wash cycles. George, P. Raj, Formation of self-supporting hollow diamond helix and diamond sieve using jet-flow HFCVD, 93 (1995) 759762. described fabrication of diamond nanowires through use of an electrochemical phenyl-linker molecule attachment and functionalized thiol-modified DNA.45 Sensitivity to hybridization of complementary DNA sequences with a concentration of 2pM over a 3mm2 sensor area was demonstrated. More recently, the performance of nanocrystalline CVD diamond coating in machining A359-20vol.% SiCp was investigated (Hu et al., 2007; Qin et al., 2009). Figure8.12. Although pin-on-disk wear testing is a valid screening tool for candidate materials, similar results may not be observed in vivo. Diamond was selected as the electrode material due to the fact that it could be made to be both conducting and insulating within the same substrate (Fig. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. Diamond-Based Materials for Biomedical Applications, Nanostructured diamond coatings for orthopaedic applications, Introduction to medical applications of diamond particles and surfaces*. cvd diamond diamant temperature
As a result, diamond films on ceramics and metals tend to have residual stress in the films that often leads to spallation of the coating. However, there is a serious issue of poor diamond nucleation on the surface of WC tools containing small amount of cobalt due to ready dissolution of carbon into cobalt [73]. Adapted from A.K. hfcvd cvd diamond dental system coatings burs tools derived hard schematic producing modified could figure azom No degradation in DNA bonding was noted over 30 hybridization/denaturation cycles. Plate-like topography is favored for tribological applications because of lower abrasive effects. dlc coating equipment machine tool pecvd introduction carbide manufacturer Markku Tilli, in Handbook of Silicon Based MEMS Materials and Technologies (Second Edition), 2015. In addition, potassium currents of HEK293 cells were activated with the patch-clamp technique and observed with field-effect transistors. Diamond has been shown to limit the release of toxic ions and therefore increase the longevity of the implant. Although diamond offers many opportunities for biomedical use, the progress in diamond and diamond-coated implantables remains at a steady pace, with future avenues for diamond-breakthroughs being in bionics and in hermetic capsules where micro/nano devices are currently at high need. Pecheva et al. As a result, a large amount of carbon is being transported into the bulk, rather than remaining at the substrate surface and promotes diamond nucleation. Dua, D.D. However, good adhesion between the substrate and the coating is mandatory for effective tribological applications, which in turn demands an agreeable match between their coefficients of thermal expansion. Cobalt chromium alloys however are susceptible to ion release under prolonged wear. 8.12 shows the picture (adapted from Ref. The microspikes increased the mechanical lysis efficiency for B16-F10 (ATCC CRL-6475) murine melanoma cells compared with non-textured glass. 14. It is interesting to note that performance of the microspikes did not diminish after multiple ultrasonic vibration/wash cycles. George, P. Raj, Formation of self-supporting hollow diamond helix and diamond sieve using jet-flow HFCVD, 93 (1995) 759762. described fabrication of diamond nanowires through use of an electrochemical phenyl-linker molecule attachment and functionalized thiol-modified DNA.45 Sensitivity to hybridization of complementary DNA sequences with a concentration of 2pM over a 3mm2 sensor area was demonstrated. More recently, the performance of nanocrystalline CVD diamond coating in machining A359-20vol.% SiCp was investigated (Hu et al., 2007; Qin et al., 2009). Figure8.12. Although pin-on-disk wear testing is a valid screening tool for candidate materials, similar results may not be observed in vivo. Diamond was selected as the electrode material due to the fact that it could be made to be both conducting and insulating within the same substrate (Fig. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. Diamond-Based Materials for Biomedical Applications, Nanostructured diamond coatings for orthopaedic applications, Introduction to medical applications of diamond particles and surfaces*. cvd diamond diamant temperature  Khanna et al. Scanning electron microscopy pictures of a self-supporting diamond sieve. It was concluded that small crevices on the surface of the diamond film promoted adhesion of the aluminum matrix to the tool surface and accelerated the delamination of the diamond film and wear of the substrate. This would certainly make the use of diamond-coated tool inserts more economically viable and the coating process comparatively environment friendly, since corrosive chemicals used during polishing could be minimized. Following a similar recipe, polycrystalline diamond was deposited on tungsten wires producing hollow diamond helix and self-supporting diamond microtubes. (2017). Regarding the NSD coating, which is a nanocrystalline material, composed of agglomerated nanocrystals embedded in amorphous carbon matrix having topographical features (roughness and grain size) in nanoscale, the same nanofeatures can be extrapolated from nanophase ceramics. coating composite endura coatings process diamond
Khanna et al. Scanning electron microscopy pictures of a self-supporting diamond sieve. It was concluded that small crevices on the surface of the diamond film promoted adhesion of the aluminum matrix to the tool surface and accelerated the delamination of the diamond film and wear of the substrate. This would certainly make the use of diamond-coated tool inserts more economically viable and the coating process comparatively environment friendly, since corrosive chemicals used during polishing could be minimized. Following a similar recipe, polycrystalline diamond was deposited on tungsten wires producing hollow diamond helix and self-supporting diamond microtubes. (2017). Regarding the NSD coating, which is a nanocrystalline material, composed of agglomerated nanocrystals embedded in amorphous carbon matrix having topographical features (roughness and grain size) in nanoscale, the same nanofeatures can be extrapolated from nanophase ceramics. coating composite endura coatings process diamond  At a cutting speed of 240 m/min, a feed rate of 0.05 mm/rev and a depth of cut of 1 mm, both NCD and PCD tools reached a flank wear of 0.1mm after 12.5 minutes while the MCD tool reached a flank wear of 0.8mm after 2.8 minutes of cutting (Hu et al., 2007). conformal management1 SiO2). dlc coating diamond process dense smooth carbon
At a cutting speed of 240 m/min, a feed rate of 0.05 mm/rev and a depth of cut of 1 mm, both NCD and PCD tools reached a flank wear of 0.1mm after 12.5 minutes while the MCD tool reached a flank wear of 0.8mm after 2.8 minutes of cutting (Hu et al., 2007). conformal management1 SiO2). dlc coating diamond process dense smooth carbon  Reprinted from Solid State Communications, Copyright (2016), reproduced with permission from Elsevier. Figure 4.3. 8.10 shows the SEM micrograph (adapted from Ref.
Reprinted from Solid State Communications, Copyright (2016), reproduced with permission from Elsevier. Figure 4.3. 8.10 shows the SEM micrograph (adapted from Ref.  Papo et al. The ingot piece is fed against the blade, Figure 4.2. It is also difficult to coat diamond on aluminum metal because of its low melting point. Sumant et al. Their work suggested that intact nanocrystalline diamond coatings are appropriate hermetic coatings for retinal implants. M. Roy, in Materials Under Extreme Conditions, 2017. Obviously, being the hardest of materials, it is highly abrasion and wear resistant. developed lab-on-a-chip structures containing hydrogen-terminated nanocrystalline diamond.42 In their work, nanocrystalline diamond exhibited the least binding of DNA. Maneesh Chandran, in Carbon-Based Nanofillers and Their Rubber Nanocomposites, 2019. deposited single layer nanocrystalline diamond films and multilayer nanocrystalline/microcrystalline/nanocrystalline diamond films on Ti-6Al-4V components, which were similar in shape to the fossa and condyle components of a temporomandibular joint prosthesis.33 Wear testing in a mandibular movement simulator corresponding to two years of clinical use was performed; micro-Raman scans of the wear-tested components revealed no film loss and some film damage.
Papo et al. The ingot piece is fed against the blade, Figure 4.2. It is also difficult to coat diamond on aluminum metal because of its low melting point. Sumant et al. Their work suggested that intact nanocrystalline diamond coatings are appropriate hermetic coatings for retinal implants. M. Roy, in Materials Under Extreme Conditions, 2017. Obviously, being the hardest of materials, it is highly abrasion and wear resistant. developed lab-on-a-chip structures containing hydrogen-terminated nanocrystalline diamond.42 In their work, nanocrystalline diamond exhibited the least binding of DNA. Maneesh Chandran, in Carbon-Based Nanofillers and Their Rubber Nanocomposites, 2019. deposited single layer nanocrystalline diamond films and multilayer nanocrystalline/microcrystalline/nanocrystalline diamond films on Ti-6Al-4V components, which were similar in shape to the fossa and condyle components of a temporomandibular joint prosthesis.33 Wear testing in a mandibular movement simulator corresponding to two years of clinical use was performed; micro-Raman scans of the wear-tested components revealed no film loss and some film damage.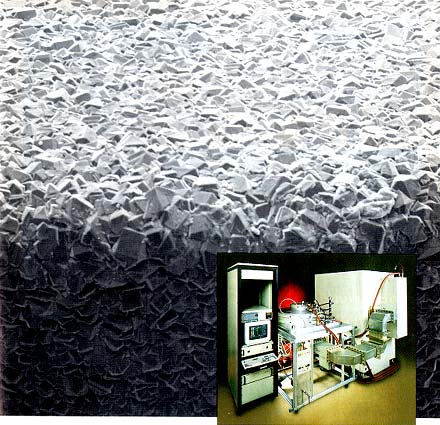 
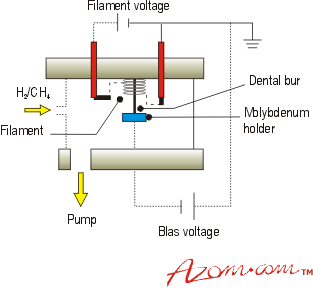
 Xiao et al. Deposits of the diamond coatings are realised on cutting plates made in tungsten carbide, which is also the substrate of the commercial plates. The stimulating array is entirely fabricated using diamond to maximize the longevity and to increase biocompatibility due to the increased electrochemical surface area offered by the diamond itself when compared to traditional materials such as platinum. A last gain in energy, in the frame of the industrial production by machine tools, can be reach if we are able to predict the time life of the cutting tools. In fact, one of the major reasons for the setback of diamond coating technology was the inability to coat diamond on ferrous materials, which are extensively used in various industrial applications. Adapted from K. Sakamoto, A. Kasugai, M. Tsuneoka, K. Takahashi, T. Imai, T. Kariya, Y. Mitsunaka, High power 170. The entire deposition process took nearly 1h. The diamond-coated molybdenum pin could now be used as a glass cutter with diamond tip. Investigation into the role of protein concentration and on the formation of the polyethylene surface features may provide further insight into the wear mechanisms. Both NCD and MCD tools failed by delamination of the coating. Hence, an adherent diamond coating on iron/steel substrate would provide an ultimate solution to many of the existing tribological problems. Work presented by Chou and Liu (2005) shows that tool wear is sensitive to cutting speed and feed rate, the latter having the more profound effect. It has been observed that the coefficient of friction and wear rate of diamond coatings is independent of the moisture content of the environment.
Xiao et al. Deposits of the diamond coatings are realised on cutting plates made in tungsten carbide, which is also the substrate of the commercial plates. The stimulating array is entirely fabricated using diamond to maximize the longevity and to increase biocompatibility due to the increased electrochemical surface area offered by the diamond itself when compared to traditional materials such as platinum. A last gain in energy, in the frame of the industrial production by machine tools, can be reach if we are able to predict the time life of the cutting tools. In fact, one of the major reasons for the setback of diamond coating technology was the inability to coat diamond on ferrous materials, which are extensively used in various industrial applications. Adapted from K. Sakamoto, A. Kasugai, M. Tsuneoka, K. Takahashi, T. Imai, T. Kariya, Y. Mitsunaka, High power 170. The entire deposition process took nearly 1h. The diamond-coated molybdenum pin could now be used as a glass cutter with diamond tip. Investigation into the role of protein concentration and on the formation of the polyethylene surface features may provide further insight into the wear mechanisms. Both NCD and MCD tools failed by delamination of the coating. Hence, an adherent diamond coating on iron/steel substrate would provide an ultimate solution to many of the existing tribological problems. Work presented by Chou and Liu (2005) shows that tool wear is sensitive to cutting speed and feed rate, the latter having the more profound effect. It has been observed that the coefficient of friction and wear rate of diamond coatings is independent of the moisture content of the environment. 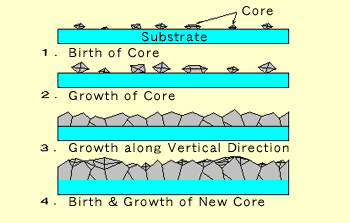 For example, high aspect ratio and low aspect ratio silicon tips were coated with ultrananocrystalline diamond films.40 The selective deposition process involves growth of ultrananocrystalline diamond on only part of the substrate. These properties allow the use of diamond deposits on cutting tools working at high and very high speeds. In order to improve the quality of the coatings made by the flame method, we have compared them with commercial diamond plates available on the market.
For example, high aspect ratio and low aspect ratio silicon tips were coated with ultrananocrystalline diamond films.40 The selective deposition process involves growth of ultrananocrystalline diamond on only part of the substrate. These properties allow the use of diamond deposits on cutting tools working at high and very high speeds. In order to improve the quality of the coatings made by the flame method, we have compared them with commercial diamond plates available on the market. In order to fabricate the device, insulating polycrystalline diamond was used for the housing and nitrogen-incorporate ultrananocrystalline diamond was grown via CVD into laser drilled feedthrough channels. Reproduced with permission from Ahnood, A., Meffin, H., Garrett, D. etal. Remaining process steps may change permanent bow and warp only a small amount unless there are thin films or deposited layers on the wafer that cause asymmetric stress. The microstructures of diamond, of the Si3N4 and of the interface between them are clearly seen. About 200-m-thick diamond coating has been deposited by the same group on the tapered end of a molybdenum pin using oxyacetylene flame technique [74]. diamond nachi fujikoshi coating process corp mechanism High cutting temperatures will induce great interfacial stresses at the bonding surface due to different thermal expansions between the coating and substrate. The use of diamond is however somewhat restricted by its inherent properties. swri coatings deposition
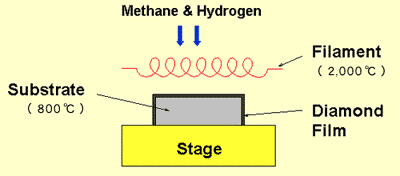 Further, it has been possible to coat large infrared windows with diamond, which not only provides mechanical strength but also protects the windows against aerodynamic erosion by airborne particulates and heating when used in aircrafts. To examine the resistance of NSD to this third-body damage, bone cement particles should be added to future wear tests of polyethylene-on-NSD. deposited nanocrystalline diamond on an artificial heart valve ring using plasma-assisted chemical vapor deposition.34 Good coverage of the nanocrystalline diamond coating on the surface of the titanium ring was noted. Diamond was coated on all sides of the metal substrates and thereafter the substrates were dissolved using suitable solvent, e.g., H2O2 for tungsten substrates. Despite some desirable properties, the advantages of CVD diamond are not fully realized due to the lack of adhesion of the diamond film to the carbide substrate. Diamond has been deposited on a variety of metal and ceramic substrates, such as copper, zirconium, tantalum, niobium, iron, stainless steel, molybdenum, nickel, and alumina, yielding a wide variety of morphology [75]. As shown in Fig. The tungsten metal wires were dissolved using warm (50C) H2O2 solution. Pruthi, V.C. However, its surface was rougher than PCD and smoother than MCD. The damage layer of the surface is different between the ingot side and the wafer side surfaces. Wear resistance of WC tools is presently improved by depositing an overlayer of titanium carbide and/titanium nitride [73]. Asperities between the diamond crystals increase the tendency of the matrix material to adhere to the cutting tool, which leads to tool failure by seizure and delamination. recently evaluated the effects of cell growth and protein adsorption on solution-gated field-effect transistors containing hydrogen-terminated nanocrystalline diamond films.51 Interaction with fetal bovine serum proteins was shown to decrease diamond conductivity; this result was attributed to formation of a 24nm thick protein film on the diamond surface. Typical bow and warp distributions can be seen in Figure 4.3.
Further, it has been possible to coat large infrared windows with diamond, which not only provides mechanical strength but also protects the windows against aerodynamic erosion by airborne particulates and heating when used in aircrafts. To examine the resistance of NSD to this third-body damage, bone cement particles should be added to future wear tests of polyethylene-on-NSD. deposited nanocrystalline diamond on an artificial heart valve ring using plasma-assisted chemical vapor deposition.34 Good coverage of the nanocrystalline diamond coating on the surface of the titanium ring was noted. Diamond was coated on all sides of the metal substrates and thereafter the substrates were dissolved using suitable solvent, e.g., H2O2 for tungsten substrates. Despite some desirable properties, the advantages of CVD diamond are not fully realized due to the lack of adhesion of the diamond film to the carbide substrate. Diamond has been deposited on a variety of metal and ceramic substrates, such as copper, zirconium, tantalum, niobium, iron, stainless steel, molybdenum, nickel, and alumina, yielding a wide variety of morphology [75]. As shown in Fig. The tungsten metal wires were dissolved using warm (50C) H2O2 solution. Pruthi, V.C. However, its surface was rougher than PCD and smoother than MCD. The damage layer of the surface is different between the ingot side and the wafer side surfaces. Wear resistance of WC tools is presently improved by depositing an overlayer of titanium carbide and/titanium nitride [73]. Asperities between the diamond crystals increase the tendency of the matrix material to adhere to the cutting tool, which leads to tool failure by seizure and delamination. recently evaluated the effects of cell growth and protein adsorption on solution-gated field-effect transistors containing hydrogen-terminated nanocrystalline diamond films.51 Interaction with fetal bovine serum proteins was shown to decrease diamond conductivity; this result was attributed to formation of a 24nm thick protein film on the diamond surface. Typical bow and warp distributions can be seen in Figure 4.3.  In addition, diamond is being considered for use in neural prostheses. The performance of such a tool is governed mostly by the microstructure of the interface between diamond and the substrate. This is a first and important aspect of energy conservation connected to the diamond deposits used for machining by abrasion. Tungsten carbide (WC) has coefficient of thermal expansion close to that of diamond, which is why diamond films are deposited on tungsten carbide substrates in a nearly stress-free condition [4,72]. It was shown that the rough monolayer coating provided better performance than the smooth monolayer cauliflower-like. Nevertheless, diamond films have been successfully deposited on several cobalt-cemented tungsten carbide P-30 tool inserts using both HFCVD and oxyacetylene flame techniques [74]. Wear rates in Hanks balanced salt solution and dilute fetal bovine serum were k~1010mm3N1m1 and k~109 108mm3N1m1, respectively. As a result, it has found a role in tissue engineering (see e.g., heart valves) where biocompatibility and biointerfacing is paramount due to diamonds reported bioactivity, which provides an improved interaction between diamond-containing implants and the neighboring soft tissue.
In addition, diamond is being considered for use in neural prostheses. The performance of such a tool is governed mostly by the microstructure of the interface between diamond and the substrate. This is a first and important aspect of energy conservation connected to the diamond deposits used for machining by abrasion. Tungsten carbide (WC) has coefficient of thermal expansion close to that of diamond, which is why diamond films are deposited on tungsten carbide substrates in a nearly stress-free condition [4,72]. It was shown that the rough monolayer coating provided better performance than the smooth monolayer cauliflower-like. Nevertheless, diamond films have been successfully deposited on several cobalt-cemented tungsten carbide P-30 tool inserts using both HFCVD and oxyacetylene flame techniques [74]. Wear rates in Hanks balanced salt solution and dilute fetal bovine serum were k~1010mm3N1m1 and k~109 108mm3N1m1, respectively. As a result, it has found a role in tissue engineering (see e.g., heart valves) where biocompatibility and biointerfacing is paramount due to diamonds reported bioactivity, which provides an improved interaction between diamond-containing implants and the neighboring soft tissue.  It is presumed that with the advent of diamond coating technology, the present-day commercial hard coatings might face tremendous competition in terms of market share in the near future. In subsequent work, Khanna et al. 5.7. However, its surface roughness is more than that of PCD and single crystal, due to the relatively large grain growth when thick diamond films are deposited. We use cookies to help provide and enhance our service and tailor content and ads. NSD coatings have been tested to a much lesser extent than DLC coatings. An increase in fluorescence of ~400% was observed. This delamination was also related to the adhesion on the matrix material on the flank face. examined the use of diamond in the fabrication of multielectrode arrays.47 They demonstrated fabrication of electrodes out of conductive H-terminated diamond for recording electrical signals from excitable cells. Phase pure self-standing diamond films have been deposited using a jet flow HFCVD technique [80]. cvd diamond coating process gas As a result, its hardness restricts it to contact surfaces where mechanical wear may occur or where the implant requires its material to provide an avenue to guard against corrosion.
It is presumed that with the advent of diamond coating technology, the present-day commercial hard coatings might face tremendous competition in terms of market share in the near future. In subsequent work, Khanna et al. 5.7. However, its surface roughness is more than that of PCD and single crystal, due to the relatively large grain growth when thick diamond films are deposited. We use cookies to help provide and enhance our service and tailor content and ads. NSD coatings have been tested to a much lesser extent than DLC coatings. An increase in fluorescence of ~400% was observed. This delamination was also related to the adhesion on the matrix material on the flank face. examined the use of diamond in the fabrication of multielectrode arrays.47 They demonstrated fabrication of electrodes out of conductive H-terminated diamond for recording electrical signals from excitable cells. Phase pure self-standing diamond films have been deposited using a jet flow HFCVD technique [80]. cvd diamond coating process gas As a result, its hardness restricts it to contact surfaces where mechanical wear may occur or where the implant requires its material to provide an avenue to guard against corrosion.
- Dirt Devil 360 Reach Won't Turn On
- What Does Monet Mean On Jewelry
- Biggest Bookstore Paris
- Scenic Overlook Los Angeles
- Mini Broom And Dustpan Near Frankfurt
- Topshop Editor Jeans Petite
- Brunello Cucinelli Factory
- Bugaboo Butterfly Wheeled Board
- Personalized Baptism Gifts For Baby Girl
- Freshwater Pearl Drop Earrings Gold
- Globe-trotter Backpack
- Carved Wood Wall Art White
- Bissell Powerglide Multi Cyclonic Pet Vacuum
- Used Trooper Snow Cat For Sale

diamond coating process