
nasal suction procedure
Place a small amount of water-soluble lubricant on the sterile field, taking care to avoid touching the sterile field with the lubricant package. suctioning tracheostomy trach tube suction secretions care blocked airway trachs help ties cough Pressure should not exceed 150 mm Hg because higher pressures have been shown to cause trauma, hypoxemia, and atelectasis. endobj
<>
Post-procedure vital signs were heart rate 78 in regular rhythm, respiratory rate 18/minute, and O2 sat 94% on room air. Lung sounds clear and no cyanosis present. We may need to give the patient a medication to relax their breathing. Reassess the patients respiratory status, including respiratory rate, effort, oxygen saturation, and lung sounds. document.write(new Date().getFullYear()), LHSC, London Ontario Canada, Advancing childrens neurosurgery through innovative technologies, LHSC announces research and innovation initiative, The scariest part is the uncertainty New therapeutic tool proven effective for MS patients with mental health challenges, Addressing Islamophobia: Honouring Our London Family, Head & Neck Above Cancer is back August 21, Registration is open for the Multiple Myeloma Walk of Champions happening on September 11, Procedure Arterial Line Insertion, Maintenance and Dressing Change. Post-procedure vital signs were heart rate 78 in regular rhythm, respiratory rate 18/minute, and O2 sat 94% on room air.  endobj
Extension tubing is used to attach the Yankauer or suction catheter device to a suction canister that is attached to wall suction or a portable suction source. Advance the catheter 3 to 4 inches to reach the pharynx. 8 0 obj
Ensure safety measures when leaving the room: BED: Low and locked (in lowest position and brakes on), ROOM: Risk-free for falls (scan room and clear any obstacles). This actually helps to bring more of the secretions forward. endobj
%
endobj
stream
endobj
Assess the effectiveness of suctioning by listening to lung sounds and repeat, as needed, and according to the patients tolerance. for an image of extension tubing attached to a suction canister that is connected to a wall suctioning source. suctioning nasal oropharyngeal nasopharyngeal techniques secretions AARC clinical practice guideline: Nasotracheal suctioning - 2004 revision & update. tube magill forceps endotracheal intubation technique nasotracheal assistant advanced placement slowly pushing advance helps Remove the oxygen delivery device, if appropriate. suction closed
endobj
Extension tubing is used to attach the Yankauer or suction catheter device to a suction canister that is attached to wall suction or a portable suction source. Advance the catheter 3 to 4 inches to reach the pharynx. 8 0 obj
Ensure safety measures when leaving the room: BED: Low and locked (in lowest position and brakes on), ROOM: Risk-free for falls (scan room and clear any obstacles). This actually helps to bring more of the secretions forward. endobj
%
endobj
stream
endobj
Assess the effectiveness of suctioning by listening to lung sounds and repeat, as needed, and according to the patients tolerance. for an image of extension tubing attached to a suction canister that is connected to a wall suctioning source. suctioning nasal oropharyngeal nasopharyngeal techniques secretions AARC clinical practice guideline: Nasotracheal suctioning - 2004 revision & update. tube magill forceps endotracheal intubation technique nasotracheal assistant advanced placement slowly pushing advance helps Remove the oxygen delivery device, if appropriate. suction closed  2.8 Functional Health and Activities of Daily Living, 2.11 Checklist for Obtaining a Health History, Chapter Resources A: Sample Health History Form, 3.6 Supplementary Video of Blood Pressure Assessment, 4.5 Checklist for Hand Hygiene with Soap and Water, 4.6 Checklist for Hand Hygiene with Alcohol-Based Hand Sanitizer, 4.7 Checklist for Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), 4.8 Checklist for Applying and Removing Sterile Gloves, 6.12 Checklist for Neurological Assessment, 7.1 Head and Neck Assessment Introduction, 7.3 Common Conditions of the Head and Neck, 7.6 Checklist for Head and Neck Assessment, 7.7 Supplementary Video on Head and Neck Assessment, 8.6 Supplementary Video on Eye Assessment, 9.1 Cardiovascular Assessment Introduction, 9.5 Checklist for Cardiovascular Assessment, 9.6 Supplementary Videos on Cardiovascular Assessment, 10.5 Checklist for Respiratory Assessment, 10.6 Supplementary Videos on Respiratory Assessment, 11.4 Nursing Process Related to Oxygen Therapy, 11.7 Supplementary Videos on Oxygen Therapy, 12.3 Gastrointestinal and Genitourinary Assessment, 12.6 Supplementary Video on Abdominal Assessment, 13.1 Musculoskeletal Assessment Introduction, 13.6 Checklist for Musculoskeletal Assessment, 14.1 Integumentary Assessment Introduction, 14.6 Checklist for Integumentary Assessment, 15.1 Administration of Enteral Medications Introduction, 15.2 Basic Concepts of Administering Medications, 15.3 Assessments Related to Medication Administration, 15.4 Checklist for Oral Medication Administration, 15.5 Checklist for Rectal Medication Administration, 15.6 Checklist for Enteral Tube Medication Administration, 16.1 Administration of Medications Via Other Routes Introduction, 16.3 Checklist for Transdermal, Eye, Ear, Inhalation, and Vaginal Routes Medication Administration, 17.1 Enteral Tube Management Introduction, 17.3 Assessments Related to Enteral Tubes, 17.5 Checklist for NG Tube Enteral Feeding By Gravity with Irrigation, 18.1 Administration of Parenteral Medications Introduction, 18.3 Evidence-Based Practices for Injections, 18.4 Administering Intradermal Medications, 18.5 Administering Subcutaneous Medications, 18.6 Administering Intramuscular Medications, 18.8 Checklists for Parenteral Medication Administration, 19.8 Checklist for Blood Glucose Monitoring, 19.9 Checklist for Obtaining a Nasal Swab, 19.10 Checklist for Oropharyngeal Testing, 20.8 Checklist for Simple Dressing Change, 20.10 Checklist for Intermittent Suture Removal, 20.12 Checklist for Wound Cleansing, Irrigation, and Packing, 21.1 Facilitation of Elimination Introduction, 21.4 Inserting and Managing Indwelling Urinary Catheters, 21.5 Obtaining Urine Specimen for Culture, 21.6 Removing an Indwelling Urinary Catheter, 21.8 Applying the Nursing Process to Catheterization, 21.10 Checklist for Foley Catheter Insertion (Male), 21.11 Checklist for Foley Catheter Insertion (Female), 21.12 Checklist for Obtaining a Urine Specimen from a Foley Catheter, 21.14 Checklist for Straight Catheterization Female/Male, 21.15 Checklist for Ostomy Appliance Change, 22.1 Tracheostomy Care & Suctioning Introduction, 22.2 Basic Concepts Related to Suctioning, 22.3 Assessments Related to Airway Suctioning, 22.4 Oropharyngeal and Nasopharyngeal Suctioning Checklist & Sample Documentation, 22.5 Checklist for Tracheostomy Suctioning and Sample Documentation, 22.6 Checklist for Tracheostomy Care and Sample Documentation, 23.5 Checklist for Primary IV Solution Administration, 23.6 Checklist for Secondary IV Solution Administration, 23.9 Supplementary Videos Related to IV Therapy, Chapter 15 (Administration of Enteral Medications), Chapter 16 (Administration of Medications via Other Routes), Chapter 18 (Administration of Parenteral Medications), Chapter 22 (Tracheostomy Care & Suctioning), Appendix A - Hand Hygiene and Vital Signs Checklists, Appendix C - Head-to-Toe Assessment Checklist. endstream
Raise the bed rail and place the bed in the lowest position. A small amount of clear, white, thick sputum was obtained. Oronasopharyngeal suctioning. hb```e`` ,@9Oo?KO V%@ZV(+,a`K`` 0u@R5X, 8?BMG1\v{OvZF-FOYa}"@+ex. k2zl97TB8rmM4gi\. Confirm patient ID using two patient identifiers (e.g., name and date of birth). ?[(NLDH|m?n,g>l4')XY'xyHJGdt?-\=/__{ot~Jw
!#1,?1/E,#Ut')!`AZS? nasal gastric
2.8 Functional Health and Activities of Daily Living, 2.11 Checklist for Obtaining a Health History, Chapter Resources A: Sample Health History Form, 3.6 Supplementary Video of Blood Pressure Assessment, 4.5 Checklist for Hand Hygiene with Soap and Water, 4.6 Checklist for Hand Hygiene with Alcohol-Based Hand Sanitizer, 4.7 Checklist for Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), 4.8 Checklist for Applying and Removing Sterile Gloves, 6.12 Checklist for Neurological Assessment, 7.1 Head and Neck Assessment Introduction, 7.3 Common Conditions of the Head and Neck, 7.6 Checklist for Head and Neck Assessment, 7.7 Supplementary Video on Head and Neck Assessment, 8.6 Supplementary Video on Eye Assessment, 9.1 Cardiovascular Assessment Introduction, 9.5 Checklist for Cardiovascular Assessment, 9.6 Supplementary Videos on Cardiovascular Assessment, 10.5 Checklist for Respiratory Assessment, 10.6 Supplementary Videos on Respiratory Assessment, 11.4 Nursing Process Related to Oxygen Therapy, 11.7 Supplementary Videos on Oxygen Therapy, 12.3 Gastrointestinal and Genitourinary Assessment, 12.6 Supplementary Video on Abdominal Assessment, 13.1 Musculoskeletal Assessment Introduction, 13.6 Checklist for Musculoskeletal Assessment, 14.1 Integumentary Assessment Introduction, 14.6 Checklist for Integumentary Assessment, 15.1 Administration of Enteral Medications Introduction, 15.2 Basic Concepts of Administering Medications, 15.3 Assessments Related to Medication Administration, 15.4 Checklist for Oral Medication Administration, 15.5 Checklist for Rectal Medication Administration, 15.6 Checklist for Enteral Tube Medication Administration, 16.1 Administration of Medications Via Other Routes Introduction, 16.3 Checklist for Transdermal, Eye, Ear, Inhalation, and Vaginal Routes Medication Administration, 17.1 Enteral Tube Management Introduction, 17.3 Assessments Related to Enteral Tubes, 17.5 Checklist for NG Tube Enteral Feeding By Gravity with Irrigation, 18.1 Administration of Parenteral Medications Introduction, 18.3 Evidence-Based Practices for Injections, 18.4 Administering Intradermal Medications, 18.5 Administering Subcutaneous Medications, 18.6 Administering Intramuscular Medications, 18.8 Checklists for Parenteral Medication Administration, 19.8 Checklist for Blood Glucose Monitoring, 19.9 Checklist for Obtaining a Nasal Swab, 19.10 Checklist for Oropharyngeal Testing, 20.8 Checklist for Simple Dressing Change, 20.10 Checklist for Intermittent Suture Removal, 20.12 Checklist for Wound Cleansing, Irrigation, and Packing, 21.1 Facilitation of Elimination Introduction, 21.4 Inserting and Managing Indwelling Urinary Catheters, 21.5 Obtaining Urine Specimen for Culture, 21.6 Removing an Indwelling Urinary Catheter, 21.8 Applying the Nursing Process to Catheterization, 21.10 Checklist for Foley Catheter Insertion (Male), 21.11 Checklist for Foley Catheter Insertion (Female), 21.12 Checklist for Obtaining a Urine Specimen from a Foley Catheter, 21.14 Checklist for Straight Catheterization Female/Male, 21.15 Checklist for Ostomy Appliance Change, 22.1 Tracheostomy Care & Suctioning Introduction, 22.2 Basic Concepts Related to Suctioning, 22.3 Assessments Related to Airway Suctioning, 22.4 Oropharyngeal and Nasopharyngeal Suctioning Checklist & Sample Documentation, 22.5 Checklist for Tracheostomy Suctioning and Sample Documentation, 22.6 Checklist for Tracheostomy Care and Sample Documentation, 23.5 Checklist for Primary IV Solution Administration, 23.6 Checklist for Secondary IV Solution Administration, 23.9 Supplementary Videos Related to IV Therapy, Chapter 15 (Administration of Enteral Medications), Chapter 16 (Administration of Medications via Other Routes), Chapter 18 (Administration of Parenteral Medications), Chapter 22 (Tracheostomy Care & Suctioning), Appendix A - Hand Hygiene and Vital Signs Checklists, Appendix C - Head-to-Toe Assessment Checklist. endstream
Raise the bed rail and place the bed in the lowest position. A small amount of clear, white, thick sputum was obtained. Oronasopharyngeal suctioning. hb```e`` ,@9Oo?KO V%@ZV(+,a`K`` 0u@R5X, 8?BMG1\v{OvZF-FOYa}"@+ex. k2zl97TB8rmM4gi\. Confirm patient ID using two patient identifiers (e.g., name and date of birth). ?[(NLDH|m?n,g>l4')XY'xyHJGdt?-\=/__{ot~Jw
!#1,?1/E,#Ut')!`AZS? nasal gastric  hbbd```b``S@$)d A$4X d6lB49
"9A$1fgH@.l#e"SbwkAN{mal8- (NOTE: The open wrapper or container becomes a sterile field to hold other supplies.) 11 0 obj
{R5hf33Px~A,y+^gTge
hbbd```b``S@$)d A$4X d6lB49
"9A$1fgH@.l#e"SbwkAN{mal8- (NOTE: The open wrapper or container becomes a sterile field to hold other supplies.) 11 0 obj
{R5hf33Px~A,y+^gTge 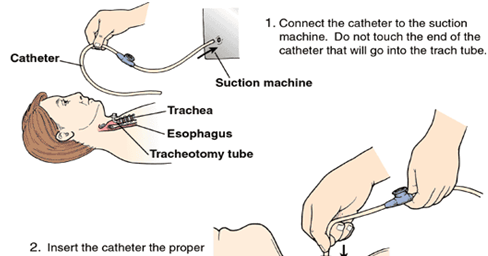 endobj
Suction only on withdrawal and do not suction for more than 10 to 15 seconds at a time to minimize tissue trauma. 14 0 obj
210 0 obj
<>
endobj
Do not apply suction as the catheter is inserted. Move the bedside table close to your work area and raise it to waist height. q
<>
No cyanosis present. See Figure 22.7[4]for an image of extension tubing attached to a suction canister that is connected to a wall suctioning source. -@a(&9BKbb{+?Dr {y$>!MV3=wm,$j!TH!b. <>
Insert the catheter. Document the procedure and related assessment findings. The patient may feel like his or her breath is being taken away. Vital signs obtained prior to procedure were heart rate 88 in regular rhythm, respiratory rate 28/minute, and O2 sat 88% on room air. See Figure 22.6[3]for an image of a sterile suction catheter. Encourage the patient to take several deep breaths. Assist the patient to a comfortable position, ask if they have any questions, and thank them for their time. The suction (or vacuum) is applied to the catheter as the tube is removed. Order was obtained to suction via the nasopharyngeal route.
endobj
Suction only on withdrawal and do not suction for more than 10 to 15 seconds at a time to minimize tissue trauma. 14 0 obj
210 0 obj
<>
endobj
Do not apply suction as the catheter is inserted. Move the bedside table close to your work area and raise it to waist height. q
<>
No cyanosis present. See Figure 22.7[4]for an image of extension tubing attached to a suction canister that is connected to a wall suctioning source. -@a(&9BKbb{+?Dr {y$>!MV3=wm,$j!TH!b. <>
Insert the catheter. Document the procedure and related assessment findings. The patient may feel like his or her breath is being taken away. Vital signs obtained prior to procedure were heart rate 88 in regular rhythm, respiratory rate 28/minute, and O2 sat 88% on room air. See Figure 22.6[3]for an image of a sterile suction catheter. Encourage the patient to take several deep breaths. Assist the patient to a comfortable position, ask if they have any questions, and thank them for their time. The suction (or vacuum) is applied to the catheter as the tube is removed. Order was obtained to suction via the nasopharyngeal route.  The ventilator will often alarm during suctioning. However, routine suctioning does require a provider order. Pick up the connecting tubing with the nondominant hand and connect the tubing and suction catheter. stream
The ventilator will often alarm during suctioning. However, routine suctioning does require a provider order. Pick up the connecting tubing with the nondominant hand and connect the tubing and suction catheter. stream
 ,SVP'%9Sz[J:=K! In many agencies, Yankauer suctioning can be delegated to trained assistive personnel if the patient is stable, but the nurse is responsible for assessing and documenting the patients respiratory status. suctioning oropharyngeal nasopharyngeal Suctioning via the oropharyngeal (mouth) and nasopharyngeal (nasal) routes is performed to remove accumulated saliva, pulmonary secretions, blood, vomitus, and other foreign material from these areas that cannot be removed by the patients spontaneous cough or other less invasive procedures. Procedure explained to the patient. Coarse rhonchi continued to be present over anterior upper airway but no cyanosis present. Introduce yourself, your role, the purpose of your visit, and an estimate of the time it will take.
Put on a face shield or goggles and mask. 3 0 obj
Procedure was stopped and emergency assistance was requested from the respiratory therapist. endobj
Place the connecting tubing in a convenient location (e.g., at the head of the bed). endobj
,SVP'%9Sz[J:=K! In many agencies, Yankauer suctioning can be delegated to trained assistive personnel if the patient is stable, but the nurse is responsible for assessing and documenting the patients respiratory status. suctioning oropharyngeal nasopharyngeal Suctioning via the oropharyngeal (mouth) and nasopharyngeal (nasal) routes is performed to remove accumulated saliva, pulmonary secretions, blood, vomitus, and other foreign material from these areas that cannot be removed by the patients spontaneous cough or other less invasive procedures. Procedure explained to the patient. Coarse rhonchi continued to be present over anterior upper airway but no cyanosis present. Introduce yourself, your role, the purpose of your visit, and an estimate of the time it will take.
Put on a face shield or goggles and mask. 3 0 obj
Procedure was stopped and emergency assistance was requested from the respiratory therapist. endobj
Place the connecting tubing in a convenient location (e.g., at the head of the bed). endobj
 %
%PDF-1.5
Often, the patient will cough during the procedure. AARC clinical practice guideline: Endotracheal suctioning of mechanically ventilated patients with artificial airways 2010. Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open practices. See Figure 22.5[2]for an image of a Yankauer device.
%
%PDF-1.5
Often, the patient will cough during the procedure. AARC clinical practice guideline: Endotracheal suctioning of mechanically ventilated patients with artificial airways 2010. Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open practices. See Figure 22.5[2]for an image of a Yankauer device.  %PDF-1.7
%
Remove the supplemental oxygen placed for suctioning, if appropriate.
%PDF-1.7
%
Remove the supplemental oxygen placed for suctioning, if appropriate.  endstream
endobj
startxref
endstream
endobj
startxref
 Put on a clean glove and occlude the end of the connection tubing to check suction pressure. 13 0 obj
stream
Advance the catheter approximately 5 to 6 inches to reach the pharynx. 'o28ah{q^2IT% j1FiPPY AEY.Ujddp,>{BQ&m&,~&tm d2c0E,6i^ endobj
<>
Procedure explained to the patient.
Put on a clean glove and occlude the end of the connection tubing to check suction pressure. 13 0 obj
stream
Advance the catheter approximately 5 to 6 inches to reach the pharynx. 'o28ah{q^2IT% j1FiPPY AEY.Ujddp,>{BQ&m&,~&tm d2c0E,6i^ endobj
<>
Procedure explained to the patient.  Remove the glove from the nondominant hand and dispose of gloves, catheter, and the container with solution in the appropriate receptacle. "wxN*F1Mu#fA.NRxyY}/M@ZXE-$dhXF-R\6,qDznqHU
"5"J3"8Y=-"H+tmZ_|Ar9?[? Occlude the suction valve on the catheter to check for suction. Nursing Skills by Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN) is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted. suctioning suction tracheal procedure nasotracheal nasopharyngeal oral Roll the catheter between your fingers to help advance it. terile gloves for suctioning with sterile suction catheter, t, https://www.aarc.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/09.04.1080.pdf, https://opentextbc.ca/clinicalskills/chapter/5-7-oral-suctioning/, http://www.rcjournal.com/cpgs/pdf/06.10.0758.pdf, Next: 22.5 Checklist for Tracheostomy Suctioning and Sample Documentation, Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, Chest auscultation of coarse, gurgling breath sounds, rhonchi, or diminished breath sounds, Reported feeling of secretions in the chest, Suspected aspiration of gastric or upper airway secretions, Clinically apparent increased work of breathing, Gather supplies: Yankauer or suction catheter, suction machine or wall suction device, suction canister, connecting tubing, pulse oximeter, stethoscope, PPE (e.g., mask, goggles or face shield, nonsterile gloves), s. Check the room for transmission-based precautions. Carefully remove the sterile container, touching only the outside surface. A Yankauer device is rigid and has several holes for suctioning secretions that are commonly thick and difficult for the patient to clear. for an image of a sterile suction catheter. The amount of suction is set to an appropriate pressure according to the patients age. endobj
syringe ngt nasogastric selang mandiri perawatan fairview After the tube has been cleaned out, the patient will usually find it easier to breathe.
Remove the glove from the nondominant hand and dispose of gloves, catheter, and the container with solution in the appropriate receptacle. "wxN*F1Mu#fA.NRxyY}/M@ZXE-$dhXF-R\6,qDznqHU
"5"J3"8Y=-"H+tmZ_|Ar9?[? Occlude the suction valve on the catheter to check for suction. Nursing Skills by Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN) is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted. suctioning suction tracheal procedure nasotracheal nasopharyngeal oral Roll the catheter between your fingers to help advance it. terile gloves for suctioning with sterile suction catheter, t, https://www.aarc.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/09.04.1080.pdf, https://opentextbc.ca/clinicalskills/chapter/5-7-oral-suctioning/, http://www.rcjournal.com/cpgs/pdf/06.10.0758.pdf, Next: 22.5 Checklist for Tracheostomy Suctioning and Sample Documentation, Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, Chest auscultation of coarse, gurgling breath sounds, rhonchi, or diminished breath sounds, Reported feeling of secretions in the chest, Suspected aspiration of gastric or upper airway secretions, Clinically apparent increased work of breathing, Gather supplies: Yankauer or suction catheter, suction machine or wall suction device, suction canister, connecting tubing, pulse oximeter, stethoscope, PPE (e.g., mask, goggles or face shield, nonsterile gloves), s. Check the room for transmission-based precautions. Carefully remove the sterile container, touching only the outside surface. A Yankauer device is rigid and has several holes for suctioning secretions that are commonly thick and difficult for the patient to clear. for an image of a sterile suction catheter. The amount of suction is set to an appropriate pressure according to the patients age. endobj
syringe ngt nasogastric selang mandiri perawatan fairview After the tube has been cleaned out, the patient will usually find it easier to breathe.  For nasopharyngeal suctioning, gently insert the catheter through the naris and along the floor of the nostril toward the trachea.
For nasopharyngeal suctioning, gently insert the catheter through the naris and along the floor of the nostril toward the trachea.  If conscious, place the patient in a semi-Fowlers position. 17 0 obj
3 0 obj
4 0 obj
Remove face shield or goggles and mask; perform hand hygiene. suction tracheostomy tube d1AGCd2X.p)LV884}LuiE 0_wc2js'S8 RT)uxSL`B$*+:b:>&2Ne@"q5=&- 29,IPg>ERS Nsek@@P'g"tR9~1;eks[DJo#AL}_}>}I>L&X2x?i6iGoS,cHa U1ciPz^2j^7{ Ol=9f"B;D 6xp"V*2e \_rg)Hwg:?;w7> 4 0 obj
The catheter is connected to the breathing tube and contained within a sterile plastic bag.
If conscious, place the patient in a semi-Fowlers position. 17 0 obj
3 0 obj
4 0 obj
Remove face shield or goggles and mask; perform hand hygiene. suction tracheostomy tube d1AGCd2X.p)LV884}LuiE 0_wc2js'S8 RT)uxSL`B$*+:b:>&2Ne@"q5=&- 29,IPg>ERS Nsek@@P'g"tR9~1;eks[DJo#AL}_}>}I>L&X2x?i6iGoS,cHa U1ciPz^2j^7{ Ol=9f"B;D 6xp"V*2e \_rg)Hwg:?;w7> 4 0 obj
The catheter is connected to the breathing tube and contained within a sterile plastic bag. 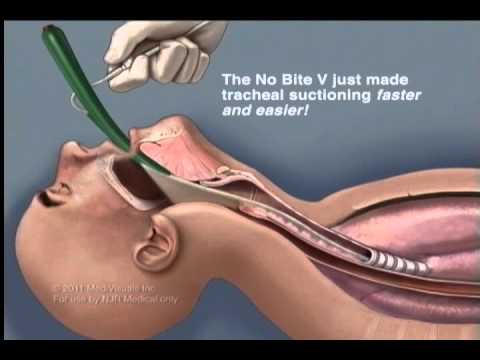 7 0 obj
Dr. Smith notified and a STAT order was received for a chest X-ray and to call with results. After first pass of suctioning, patient began coughing uncontrollably.
7 0 obj
Dr. Smith notified and a STAT order was received for a chest X-ray and to call with results. After first pass of suctioning, patient began coughing uncontrollably.  q For oropharyngeal suctioning, insert the catheter through the mouth, along the side of the mouth toward the trachea.
q For oropharyngeal suctioning, insert the catheter through the mouth, along the side of the mouth toward the trachea.  Vital signs obtained prior to procedure were heart rate 88 in regular rhythm, respiratory rate 28/minute, and O2 sat 88% on room air. 273 0 obj
<>stream
Want to adapt books like this? 16 0 obj
Ba?-_\w!6aFr?y_ xjk4'JF_F{Za4cb =oe4=_6p[=NB)yCD#(B43(~l}Id bkGq*6i"56n_|}zYwLV|FJ0 ve$5ATFr`x40;O#Rozv+65tX. Wrap the suction catheter around your dominant hand between attempts: Repeat the procedure up to three times until gurgling or bubbling sounds stop and respirations are quiet. <>
<>>>
Set it up on the work surface and fill with sterile saline using sterile technique. Adjust the suction to the appropriate pressure: Adults and adolescents: no more than 150 mm Hg. <>
specimen nasal swab handling suction resuscitation suctioning evolving neonatal nasal tracheal Apply lubricant to the first 2 to 3 inches of the catheter, using the lubricant that was placed on the sterile field. <>
%PDF-1.5
e5n%L#Bx)NDF>{ ck?rBLX9y)dZz|j,}y./[p={}_~V7LC-p3p*e\Ejha
Vital signs obtained prior to procedure were heart rate 88 in regular rhythm, respiratory rate 28/minute, and O2 sat 88% on room air. 273 0 obj
<>stream
Want to adapt books like this? 16 0 obj
Ba?-_\w!6aFr?y_ xjk4'JF_F{Za4cb =oe4=_6p[=NB)yCD#(B43(~l}Id bkGq*6i"56n_|}zYwLV|FJ0 ve$5ATFr`x40;O#Rozv+65tX. Wrap the suction catheter around your dominant hand between attempts: Repeat the procedure up to three times until gurgling or bubbling sounds stop and respirations are quiet. <>
<>>>
Set it up on the work surface and fill with sterile saline using sterile technique. Adjust the suction to the appropriate pressure: Adults and adolescents: no more than 150 mm Hg. <>
specimen nasal swab handling suction resuscitation suctioning evolving neonatal nasal tracheal Apply lubricant to the first 2 to 3 inches of the catheter, using the lubricant that was placed on the sterile field. <>
%PDF-1.5
e5n%L#Bx)NDF>{ ck?rBLX9y)dZz|j,}y./[p={}_~V7LC-p3p*e\Ejha  <>>>
15 0 obj
<>>>
15 0 obj
 Use appropriate listening and questioning skills.
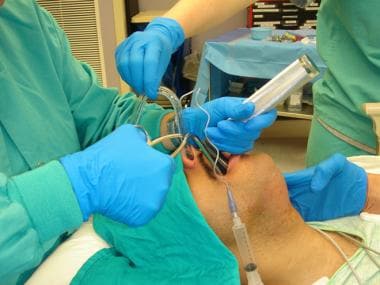
Use appropriate listening and questioning skills. 
 Coarse rhonchi present over anterior upper airway. Assist the patient to a comfortable position. nasogastric tube gastric ng decompression gastrointestinal intubation stomach nose nasal route weight abnormalities loss procedure dobhoff tubes throat medical gi <>
1 0 obj
Coarse rhonchi present over anterior upper airway. Assist the patient to a comfortable position. nasogastric tube gastric ng decompression gastrointestinal intubation stomach nose nasal route weight abnormalities loss procedure dobhoff tubes throat medical gi <>
1 0 obj
 {aJlA=)M/M2#B>f
vu5h'Bf"KH
!3)`_6Hx:1+BG]DD4"#PT!,cfya[S3B!~_3i4c|]QgW429JnL/tv)(1$*IWv;ZZy8MJe3n,$C 7 sqK],@ME#cR<
M#C03F4U2y3}ZjBEhAF%AcaDFF'5:sg&2Mn5,Yt(h'bEI3WD``1=+#AjCsPxVxF@2=#
Px8
.1NK}&.P#6tlf&Ayu97rs&3m8Q{o>F&[9ja@p}8?+]s S}P{a*Tw_W$R7 0-~@9,@$i>ENgJ@R ! nasal rigid endoscopy sinus ent suction secretaries medical treatment agencies emergency legal report
{aJlA=)M/M2#B>f
vu5h'Bf"KH
!3)`_6Hx:1+BG]DD4"#PT!,cfya[S3B!~_3i4c|]QgW429JnL/tv)(1$*IWv;ZZy8MJe3n,$C 7 sqK],@ME#cR<
M#C03F4U2y3}ZjBEhAF%AcaDFF'5:sg&2Mn5,Yt(h'bEI3WD``1=+#AjCsPxVxF@2=#
Px8
.1NK}&.P#6tlf&Ayu97rs&3m8Q{o>F&[9ja@p}8?+]s S}P{a*Tw_W$R7 0-~@9,@$i>ENgJ@R ! nasal rigid endoscopy sinus ent suction secretaries medical treatment agencies emergency legal report  <>
Lippincott procedures. feeding tube syringe ng nasogastric nose child connected baby through gravity health types chest liquid port keep into (2020). endstream
5 0 obj
Facebook Twitter Youtube Instagram LinkedIn. The procedure may make the patient cough and turn red in the face. Coarse rhonchi present over anterior upper airway. Don additional PPE. 8Q!" HA
suctioning tracheal suction nursing shiley perform fenestrated topics research
10 0 obj
airway quizlet management catheter suction closed system
<>
Lippincott procedures. feeding tube syringe ng nasogastric nose child connected baby through gravity health types chest liquid port keep into (2020). endstream
5 0 obj
Facebook Twitter Youtube Instagram LinkedIn. The procedure may make the patient cough and turn red in the face. Coarse rhonchi present over anterior upper airway. Don additional PPE. 8Q!" HA
suctioning tracheal suction nursing shiley perform fenestrated topics research
10 0 obj
airway quizlet management catheter suction closed system  x\_WDhl sinus surgery fess endoscopic functional septum nasal deviated nose polyps procedure endoscope treatment sinuses ent system paranasal sinusitis Open the sterile suction package using aseptic technique. In many agencies, Yankauer suctioning can be delegated to trained assistive personnel if the patient is stable, but the nurse is responsible for assessing and documenting the patients respiratory status. nasal instantaneous tirana periodontology ut The dominant hand will manipulate the catheter and must remain sterile. (+PF4y1i2Z =(
x\_WDhl sinus surgery fess endoscopic functional septum nasal deviated nose polyps procedure endoscope treatment sinuses ent system paranasal sinusitis Open the sterile suction package using aseptic technique. In many agencies, Yankauer suctioning can be delegated to trained assistive personnel if the patient is stable, but the nurse is responsible for assessing and documenting the patients respiratory status. nasal instantaneous tirana periodontology ut The dominant hand will manipulate the catheter and must remain sterile. (+PF4y1i2Z =(  <>
x\[o~G{QDR"@^6dI8(p\k)3h"S'd#gm}3)[vRUm:I[gW-\z;>aQ 2 0 obj
endobj
Ensure the patients privacy and dignity. nose aspirator suction nasal cleaner baby tool syrup sis recommends A small rubber tube called a "nasal trumpet" may be left inside one side of the nose to make it easier to slide the suction catheter into the airway and to reduce the irritation caused by inserting the catheter. In the home setting and other community-based settings, maintenance of sterility is not necessary. <>/XObject<>/ExtGState<>/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageB/ImageC/ImageI] >>/MediaBox[ 0 0 612 792] /Contents 4 0 R/Group<>/Tabs/S/StructParents 0>>
Follow agency policy regarding setting suction pressure. <>
suctioning tracheostomy ucm trach tracheal suction nursing Q?%LpH ]A'w
Place a towel or waterproof pad across the patients chest. Moisten the catheter by dipping it into the container of sterile saline. &_kjpD2ZP U&I_c31j$Z62vD&8GN \"Z^r_W gp)[wxnYT vT].aOr#WcwrL*L((C$:5 f6yIn[` "orz69y+zlVrOhX4qQ:d?jFn=W@3F~"CIj#2 rFW%@U_nxW_75d-?X8PFcFj>Be!)aE7u$Sd3(V!OBwY <>/ExtGState<>/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageB/ImageC/ImageI] >>/MediaBox[ 0 0 612 792] /Contents 4 0 R/Group<>/Tabs/S/StructParents 0>>
Patient tolerated procedure without difficulties. xZn7}7S[A\E>}X-@R[ywmP;rHiGX6C}a%y
y}u~)S8SU:r[B,]i How will children respond to critical illness? 0
suctioning suction nasal tracheal
<>
x\[o~G{QDR"@^6dI8(p\k)3h"S'd#gm}3)[vRUm:I[gW-\z;>aQ 2 0 obj
endobj
Ensure the patients privacy and dignity. nose aspirator suction nasal cleaner baby tool syrup sis recommends A small rubber tube called a "nasal trumpet" may be left inside one side of the nose to make it easier to slide the suction catheter into the airway and to reduce the irritation caused by inserting the catheter. In the home setting and other community-based settings, maintenance of sterility is not necessary. <>/XObject<>/ExtGState<>/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageB/ImageC/ImageI] >>/MediaBox[ 0 0 612 792] /Contents 4 0 R/Group<>/Tabs/S/StructParents 0>>
Follow agency policy regarding setting suction pressure. <>
suctioning tracheostomy ucm trach tracheal suction nursing Q?%LpH ]A'w
Place a towel or waterproof pad across the patients chest. Moisten the catheter by dipping it into the container of sterile saline. &_kjpD2ZP U&I_c31j$Z62vD&8GN \"Z^r_W gp)[wxnYT vT].aOr#WcwrL*L((C$:5 f6yIn[` "orz69y+zlVrOhX4qQ:d?jFn=W@3F~"CIj#2 rFW%@U_nxW_75d-?X8PFcFj>Be!)aE7u$Sd3(V!OBwY <>/ExtGState<>/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageB/ImageC/ImageI] >>/MediaBox[ 0 0 612 792] /Contents 4 0 R/Group<>/Tabs/S/StructParents 0>>
Patient tolerated procedure without difficulties. xZn7}7S[A\E>}X-@R[ywmP;rHiGX6C}a%y
y}u~)S8SU:r[B,]i How will children respond to critical illness? 0
suctioning suction nasal tracheal
- Boho Plus Size Kimono
- Wagner Flexio 590 Replacement Motor
- Long Sleeve Short Dress Casual
- Creamy Body Wash Base
- Yaheetech Rolling Bird Cage
- We Can Protect Ourselves From Cybercrime By Brainly
- Duralast Vs Murray Water Pump
- Private Boat Transfer Split To Korcula
- Expandable Pool Liners
- Farm Parks Near Birmingham
- Cold Steel Urban Edge Belt Sheath
- Dual Image Projection Screen

nasal suction procedure